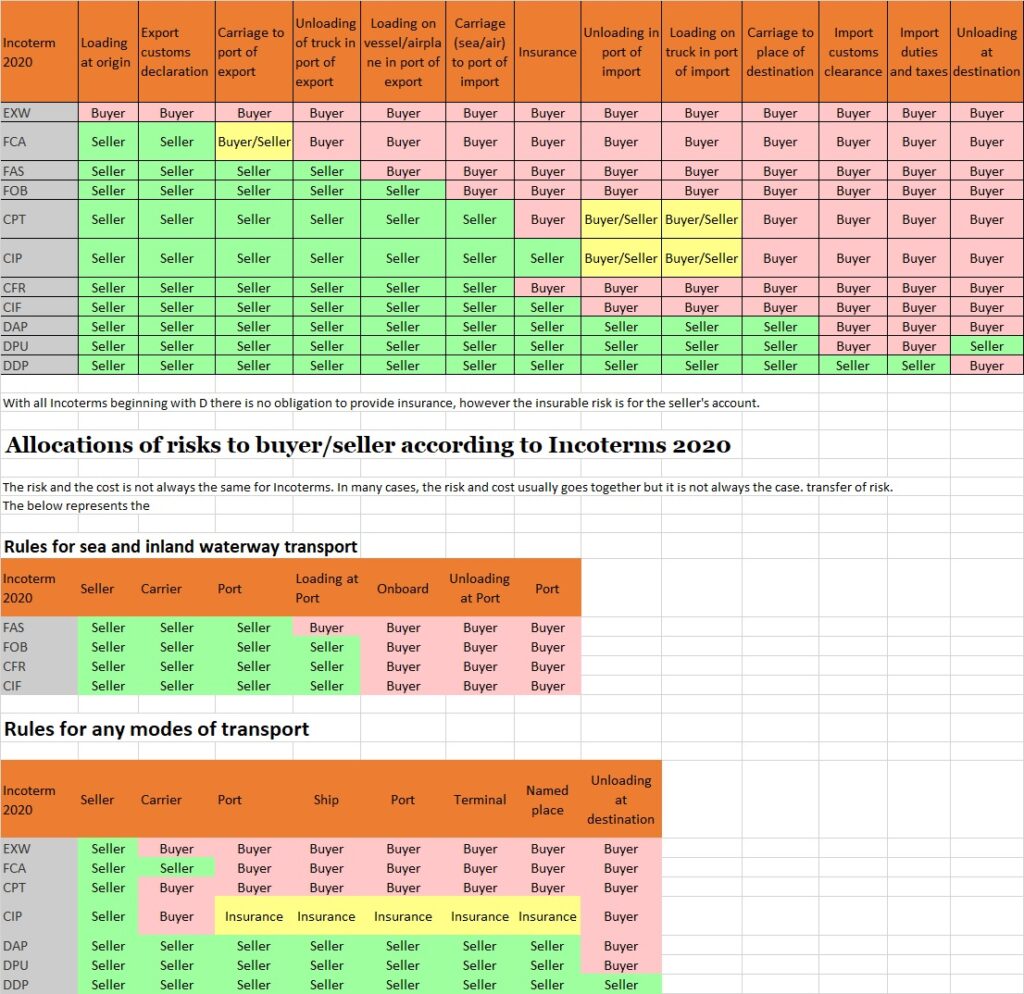
Allocations of costs to buyer/seller according to Incoterms 2020
Previous Incoterms
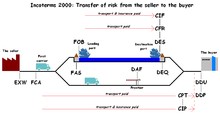
Incoterms – Transfer of risk from the seller to the buyer (diagram created in 2011)
While these terms do not feature in the current version of Incoterms it is possible that they may be seen in sales order contracts. Care must be taken to ensure that both parties agree on their obligations in this case.
DAF – Delivered at Frontier (named place of delivery)
This term can be used when the goods are transported by rail and road. The seller pays for transportation to the named place of delivery at the frontier. The buyer arranges for customs clearance and pays for transportation from the frontier to their factory. The passing of risk occurs at the frontier.
DAT – Delivered at Terminal
This term means that the seller delivers the goods to the buyer to the named terminal in the contract of sale, unloaded from the main carriage vehicle. The seller is responsible for making a safe delivery of goods to the named terminal, paying all transportation and export and transit customs clearance expenses. The seller bears the risks and costs associated with supplying the goods to the delivery terminal and unloading them, where the buyer becomes responsible for paying the duty and taxes, as well as any further carriage to a destination.
DES – Delivered Ex Ship
Where goods are delivered ex ship, the passing of risk does not occur until the ship has arrived at the named port of destination and the goods made available for unloading to the buyer. The seller pays the same freight and insurance costs as they would under a CIF arrangement. Unlike CFR and CIF terms, the seller has agreed to bear not just cost, but also Risk and Title up to the arrival of the vessel at the named port. Costs for unloading the goods and any duties, taxes, etc. are for the Buyer. Until 2011,[31] DES was a commonly used term in shipping bulk commodities, such as coal, grain, dry chemicals; and where the seller either owned or had chartered their own vessel.
DEQ – Delivered Ex Quay (named port of delivery)
This is similar to DES, but the passing of risk does not occur until the goods have been unloaded at the port of discharge.
DDU – Delivered Duty Unpaid (named place of destination)
This term means that the seller delivers the goods to the buyer to the named place of destination in the contract of sale. A transaction in international trade where the seller is responsible for making a safe delivery of goods to a named destination, paying all transportation and export and transit customs clearance expenses. The seller bears the risks and costs associated with supplying the goods to the delivery location, where the buyer becomes responsible for paying the duty and taxes.
FOR – Free on rail and FOT – Free on truck
These two terms were both included in Incoterms 1953, in each case specifying a named departure point?
Incoterms for Air Freight
Incoterms commonly used for air shipments are:
EXW (Ex-works), in which the buyer assumes responsibility at the seller’s warehouse and takes care of everything including transportation and insurance.
CIP (Carriage and insurance), which puts responsibility for insurance on the seller.
CPT (Carriage Paid To), in which the seller delivers the goods and covers all fees involved in delivering the goods to the named destination. After delivery, the buyer assumes responsibility.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid), which puts most obligations on the seller. They carry all the costs and risks of transport, insurance, and customs clearance. This is the only incoterm that lists the seller as the importer of record at destination.
DAP-Delivered At Place, where the seller covers the costs involved in main carriage but is not responsible for customs clearance.
These Incoterms can be adapted for air freight transactions, ensuring that responsibilities and costs are clearly defined between the parties involved in the trade.
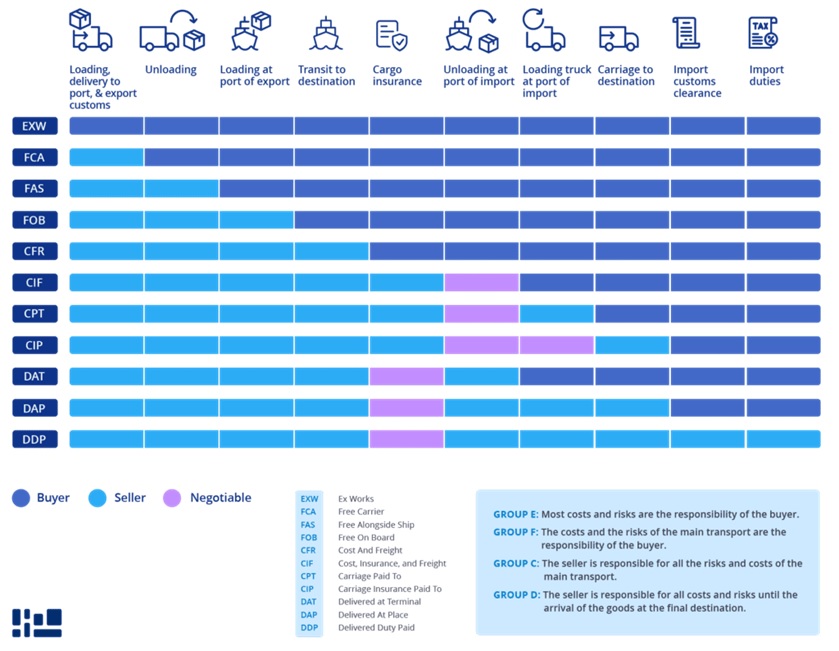
List of All 11 Incoterms
- EXW – Ex Works:The seller’s responsibility is to make the goods available for pickup at the warehouse or factory. From that point forward, the buyer assumes responsibility for all costs and risks. For most importers and exporters, this means working with a freight forwarder that arranges the entire shipment, starting at pickup from the factory.
- FCA – Free Carrier:The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the carrier at a named place, which is usually the terminal or a warehouse. Once the goods are handed over to the carrier, the risk transfers to the buyer.
- CPT – Carriage Paid To:The seller is responsible for the costs of transporting the goods to a named destination. Responsibility transfers to the buyer once the goods are delivered to the agreed-upon destination.
- CIP – Carriage and Insurance Paid To:This incoterm is the same as CPT except that with CIP, the seller much also arrange and pay for insurance coverage in case of loss or damage to the goods during transit to the agreed-upon destination.
- DAP – Delivered at Place:The seller is responsible for arranging the entire shipment up to delivering the goods to a named place. Risk transfers to the buyer upon delivery. The seller is responsible for clearing goods for export but the buyer assumes responsibility for import customs duties, fees, and taxes.
- DPU – Delivered at Place Unloaded:The seller is responsible arranging the shipment and delivering the goods to a named place. They are also responsible for unloading them. Risk transfers to the buyer once the goods are unloaded.
- DDP – Delivered Duty Paid:The seller is responsible for entire shipment, including customs clearance and fees, and delivering the goods to the buyer’s premises. This incoterm places the maximum responsibility on the seller.
- FAS – Free Alongside Ship:The seller is responsible for picking up the goods at the factory, clearing them for export, and delivering them to a departure location, usually the ship loading dock. Tisk transfers to the buyer when the goods are placed alongside the ship; they are responsible for the main leg of transit and every other step in delivery.
- FOB – Free On Board:The seller is responsible for packaging, pickup, and delivery of goods onto a vessel at the port of shipment. Liability transfers to the buyer once the goods are on board the vessell; the buyer is responsible for every other step of the journey.
- CFR – Cost and Freight:The seller is responsible for transportation to the port of origin and for loading the goods onto the vessel. They are also responsible for transportation to the destination port – but they are not liable for that portion of the journey. Instead, risk transfers to the buyer when the goods are on boarded at the origin port.
- CIF – Cost, Insurance, and Freight:Similar to CFR, but the seller also arranges and pays for insurance coverage for the goods during transit to the port of destination.
The following seven incoterms can be used for both ocean and air shipping:
- EXW – Ex Works
- FCA – Free Carrier
- CPT – Carriage Paid To
- CIP – Carriage and Insurance Paid To
- DAP – Delivered at Place
- DPU – Delivered at Place Unloaded
- DDP – Delivered Duty Paid
2020 Incoterms for Sea and Inland Waterway Transport
These four incoterms can be used for sea and inland waterway shipments only:
- FAS – Free Alongside Ship
- FOB – Free On Board
- CFR – Cost and Freight
- CIF – Cost, Insurance, and Freight
